Cécile LE FLOCH-FOUERE
cecile.lefloch-fouere@institut-agro.fr
Stéphane PEZENNEC
stephane.pezennec@inrae.fr
Our objectives
Our molecules of choice are proteins and we are also interested in their interactions with other types of molecules.
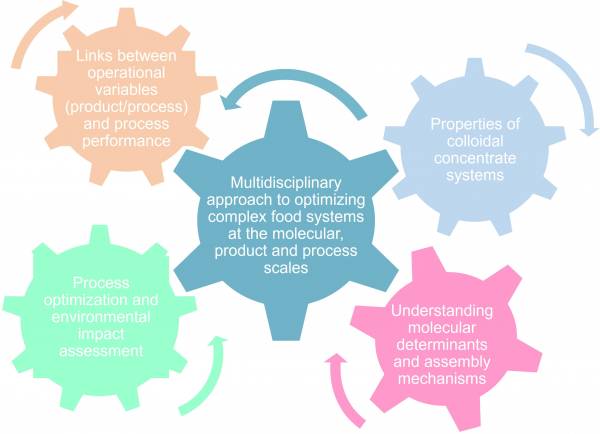
Our research focuses on :
- molecular determinants and mechanisms of supramolecular assembly and phase separation ;
- The properties (interactions, osmotic pressure, reversibility, stability, sol-gel transition, etc.) of concentrated colloidal systems used in various unit operations such as filtration, concentration by evaporation or drying;
- links between operating variables (process - product) and the performance of food processes;
- optimisation of the design, control and sequence of unitary processing operations, and assessment of the corresponding environmental impacts.
Our Strategy
Our generic and mechanistic research questions are enriched and fed by technological issues and are tackled by developing our studies at different scales, from the molecular to the macroscopic one, and by alternating model and real systems, so as to:
- explore the main molecular and supramolecular mechanisms (interactions, assemblies, phase separation) behind the macroscopic behaviour of food proteins;
- identify, quantify and model the physico-chemical mechanisms involved in the state transitions undergone by dairy matrices during concentration and 'deconcentration' operations;
- decouple the unit operations of a dairy and cheese technological route in order to control and optimise the properties of these matrices;
- develop approaches to help the design and the conception of processes using multi-criteria approaches;
- capitalise on this knowledge, using a predictive approach, for processes that reconcile performance, environmental impacts and product quality.
Our expertise
The team's disciplinary skills are:
- Process engineering
- biochemistry and physical chemistry
- rheology
- soft matter physics applied to food matrices
- dairy science and technology.
Our team
Technicians/Assistant engineers : Françoise BOISSEL, Thomas CANIQUIT, Jean-Jacques DUBOIS, Anne DOLIVET, Pascaline HAMON, Fabienne LAMBROUIN, Nadine LECONTE, Pascal LECOUILLARD, Arlette LEDUC
Engineers : Gilles GARRIC, Emeline GOUSSÉ, Fanny GUYOMARC’H, Mélanie MUNCH, Florence ROUSSEAU, Gaëlle TANGUY, Anny VIVAS-ABRIL
Scientists : Ghazi BEN MESSAOUD, Saïd BOUHALLAB, Thomas CROGUENNEC, Marie-Hélène FAMELART, Juliane FLOURY, Geneviève GÉSAN-GUIZIOU, Romain JEANTET, Luca LANOTTE, Valérie LECHEVALIER, Jeehyun LEE, Cécile LE FLOCH-FOUÉRÉ, Maksym LOGINOV, Stéphane PEZENNEC
Our PhD and post-doctoral students
- ALMEIDA Jaqueline (PhD, november 2025 - august 2026) : CAPES-COFECUB LacFree. Supervision: GOUSSE Emeline.
- CORDIN Ulysse (PhD)-Supervision: FLOURY Juliane/GESAN-GUIZIOU Geneviève/GUYOMARC'H Fanny. Start of PhD: 2025. "Accounting for scale change in the environmental assessment of food transformation processes".
- BARBOSA Letícia (PhD, september 2025 - june 2026): CAPES-COFECUB LacFree. Supervision: TANGUY Gaëlle.
- MOREL Johanna (PhD)-Supervision: CROGUENNEC Thomas/JEANTET Romain/LANOTTE Luca/BEN MESSAOUD Ghazi/PEZENNEC Stéphane. Start of PhD: 2025. "Optimising the energy performance of dairy ingredient manufacturing processes".
- LE FOLL Rozenn (Post-doc, 2024–2025): Calaccess, Supervision : DUPONT Didier/CROGUENNEC Thomas.
- JAGOREL Gabrielle (fixed term contract, 2024–2026): ANR Veg&Lait, Supervision: GUYOMARC’H Fanny.
- OUYANG Rui (PhD)-Supervision: LE FLOCH-FOUERE Cécile/LANOTTE Luca. Start of PhD: 2024. "Multi-scale exploration of the drying dynamics of dairy colloids and their rehydration (DRYMAP) Exploration of evaporation kinetics and modelling of stratification of dairy colloid mixtures during drying (DRYMAP)".
- RABESOLONIRINA Tanjona (PhD)-Supervision: LE FLOCH-FOUERE Cécile. Start of PhD: 2024. "How do the surface conditions of moulds and curds affect adhesion during cheese production?".
- JUSTE Erik (PhD)-Supervision: CROGUENNEC Thomas/LEE Jeehyun. Start of PhD: 2023. Poster: How whey protein aggregates interfer on milk enzymatic and acid gelation?
- GROSTETE Margot (PhD )Supervision: LANOTTE Luca/JEANTET Romain. Start of PhD: 2022. Poster: Understanding the fouling mechanisms in evaporators...
- PERRIGNON Manon (PhD)-Supervision: CROGUENNEC Thomas/JEANTET Romain. Start of PhD: 2022. Poster : Statistical approach for the optimization of dairy industrial...
Our visiting professors
- TULER PERRONE Italo (2025), professsor, Federal University of Juiz de Fora (BRA), CAPES-COFECUB LacFree
Our projects
VEG&LAIT: The VEG&LAIT project aims to co-construct a mini-sector of mixed desserts based on milk and legumes, produced and processed in local food networks to reconcile autonomy, taste and nutritional qualities, environmental preservation and maintaining a close link with consumers. It started in March 2024 and will go on for 5 years, supported by the ANR-23-PLEG-0006 grant from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche as part of the France 2030 investment plan. Five INRAE units are involved (Agronomy, CSGA, ETTIS, SECALIM and STLO) with Invitation à la Ferme, Terres Inovia and Valorex, and the support of the LEGGO Association.
DIMEMPRO (2022-2025): Sizing strategy for optimising membrane process design. DIMEMPRO is a project funded by CARNOT QUALIMENT. It aims to develop a reasoned sizing methodology for membrane operations with a view to optimising the multi-criteria design of processes in the dairy sector.
FLait: Modelling the transmission of serum proteins during microfiltration of skimmed milk - Thesis co-funded by the INRAE-TRANSFORM department and the Brittany Region
STATPERF: A statistical approach to optimising business performance. This project studies the potential of artificial intelligence tools for optimising the overall performance (product quality, manufacturing yields, environmental impact, etc.) of the cheese-making process. Manon Perrignon's PhD. Funding: Institut Agro Fondation
TEX'AS: By what mechanisms do whey protein aggregates affect the coagulation properties of milk? This project studies the role of protein aggregates on the characteristics of milk gels and on gelling mechanisms. Erik Juste's PhD. Funding: CIFRE
ENTEVAP: Understanding the mechanisms of thermal fouling in falling-flow evaporators using a microfluidic and microscopic approach. The aim of the project is to put in place a miniaturisation strategy to characterise the constituents preferentially involved in the development of fouling, identify the process parameters with the most marked influence on the stages of deposit formation and, possibly, propose control methods to limit this phenomenon, which has very costly consequences for various sectors of food production. In this context, Margot Grostete's PhD, funded by ARED/TRANSFORM, focuses mainly on assessing the role of shear in the initiation and propagation of the phenomenon of milk protein deposition on surfaces with different properties (glass, steel) using rheometry and microfluidic tests coupled with microscopic observation.